Giáo án Tiếng Anh Khối 7 - Bài 12: An overcrowded world (Một thế giới quá đông đúc)
I. SO SÁNH VỀ SỐ LƯỢNG VỚI “MORE/LESS/FEWER”(COMPARISONS OF QUANTIFIERS)
1. Các lượng từ “more/less/fewer” (nhiều hơn/ ít hơn/ ít hơn)
- More (nhiều hơn): là dạng so sánh hơn của “many” và “much”.
- Less, fewer (ít hơn): “less” là biến đổi của “little”, còn “fewer” là biến đổi của “few”.
- “more” dùng để so sánh số lượng vật này nhiều hơn vật kia, còn “fewer” và “less” được dùng để so sánh số lượng vật này ít hơn vật kia.
2. Cấu trúc
Bạn đang xem 20 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Giáo án Tiếng Anh Khối 7 - Bài 12: An overcrowded world (Một thế giới quá đông đúc)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
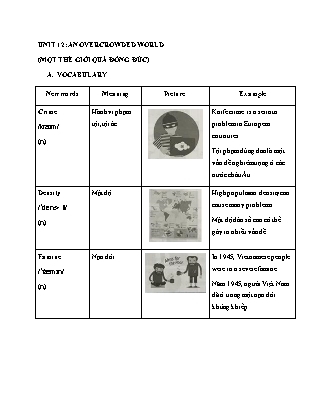
UNIT 12: AN OVERCROWDED WORLD (MỘT THẾ GIỚI QUÁ ĐÔNG ĐÚC) VOCABULARY New words Meaning Picture Example Crime /kraɪm/ (n) Hành vi phạm tội, tội ác Knife crime is a serious problem in European countries. Tội phạm dùng dao là một vấn đề nghiêm trọng ở các nước châu Âu. Density /ˈdensəti/ (n) Mật độ High population density can cause many problems. Mật độ dân số cao có thể gây ra nhiều vấn đề. Famine /ˈfæmɪn/ (n) Nạn đói In 1945, Vietnamese people were in a severe famine. Năm 1945, người Việt Nam đã ở trong một nạn đói khủng khiếp. Health care /ˈhelθ ˌkeə(r)/ (n) Chăm sóc sức khỏe The government will reduce the costs of health care for poor people. Chính phủ sẽ cắt giảm chi phí chăm sóc sức khỏe cho người nghèo. Issue /ˈɪʃuː/ (n) Vấn đề It is a big issue, we shouldn’t ignore it. Đó là một vấn đề lớn, chúng ta không nên bỏ qua nó. Standard of living /ˌstændəd əv ˈlɪvɪŋ/ (n) Mức sống Mức sống của con người bây giờ cao hơn trước kia. Megacity /ˈmeɡəsɪti/ (n) Siêu đô thị Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh là siêu đô thị đầu tiên của Việt Nam. Overcrowded /ˌəʊvəˈkraʊdɪd/ (adj) Quá đông đúc, đông nghịt Ở Hà Nội, có nhiều người đang sống trong tình trạng quá đông đúc. Physician /fɪˈzɪʃ.ən/ (n) Bác sĩ (người chuyên điều trị mà không dùng phẫu thuật) Ông ấy trở thành bác sĩ riêng của Tổng thống vào năm 1995 Poverty /ˈpɒvəti/ (n) Sự đói nghèo Có rất nhiều người già đang sống trong đói nghèo. Slavery /ˈsleɪvəri/ (n) Tình trạng nô lệ Họ từng sống trong cảnh nô lệ và nghèo đói. Slum /slʌm/ (n) Nhà ổ chuột Thường có vài khu ổ chuột ở những thành phố lớn. Spacious /ˈspeɪʃəs/ (adj) Rộng rãi The hotel rooms are spacious and comfortable. Phòng khách sạn rất rộng rãi và thoải mái. Underdeveloped /ˌʌndədɪˈveləpt/ (n) Chưa phát triển People in underdeveloped countries have low standards of living. Người dân ở những nước chưa phát triển có mức sống thấp. Wealthy /welθi/ (adj) Giàu có America is a wealthy nation. Mỹ là một quốc gia giàu có. GRAMMAR SO SÁNH VỀ SỐ LƯỢNG VỚI “MORE/LESS/FEWER”(COMPARISONS OF QUANTIFIERS) Các lượng từ “more/less/fewer” (nhiều hơn/ ít hơn/ ít hơn) More (nhiều hơn): là dạng so sánh hơn của “many” và “much”. Less, fewer (ít hơn): “less” là biến đổi của “little”, còn “fewer” là biến đổi của “few”. “more” dùng để so sánh số lượng vật này nhiều hơn vật kia, còn “fewer” và “less” được dùng để so sánh số lượng vật này ít hơn vật kia. Cấu trúc So sánh (Danh từ đếm được và danh từ không đếm được) + more+ danh từ + than+ VD: The countryside has more trees than a big city. (Vùng quê có nhiều cây hơn thành phố lớn.) This city has more traffic than that one. (Thành phố này có xe cộ đi lại nhiều hơn thành phố kia.) So sánh kém (Danh từ đếm được) + fewer + danh từ đếm được số nhiều (-s/es) + than+ VD: The countryside has fewer problems trees than a big city. (Vùng quê có ít vấn đề hơn thành phố lớn) So sánh kém (Danh từ không đếm được) + less + danh từ không đếm được + than+ VD: I have less money than you. (Tôi có ít tiền hơn bạn) BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN Bài 1: Khoanh tròn đáp án đúng. I have (less/ fewer) pocket money than my brother. He eats (less/ fewer) vegetables and fruit than his wife. The doctor advised the kid to eat (less/ fewer) sweets to be healthy. There are (less/ fewer) cars in this town than in my city. Mr. Smith does (less/ fewer) exercise than he should. She has (less/ fewer) patience than her coworker. I have (less/ fewer) time to spend on relaxing than my sister. Peter wants to have (less/ fewer) business trips because he has become seriously weak. She has (less/ fewer) work to do than me. The students have (less/ fewer) days to finish the project. Jack is advised to smoke (less/ fewer) cigarettes. Jane has (less/ fewer) friends than Jim. My city has (less/ fewer) friends than Jim. There are (less/ fewer) tourists this year. Peter has (less/ fewer) toys than his sibings. Bài 2: Điền “more/less/fewer” vào chỗ trống sao cho hợp lý. My company has _____fewer_______ employees than your company because mine has about one hundred employees but yours has almost two hundred. ( Công ty của tôi có ít nhân viên hơn của bạn vì công ty tôi có khoảng 100 nhân viên nhưng công ty bạn lại có gần 200) Jim learns better than Jane. He has __more__________ good grades than Jane. Jim học tốt hơn Jane. Cậu ấy có nhiều điểm tốt hơn Jane Because of water pollution, nowadays there is ___less___ fresh water than in the past. Do ôi nhiễm nguồn nước , ngày nay có ít nước sạch hơn trước kia. My neighborhood is more peaceful than your neighborhood. Yours has criminal cases than mine. Khu dân cư của tôi yên bình hơn của bạn. Của bạn có nhiều trường hợp phạm tội hơn của tôi. There are ____more________ industrial emissions in the city than in the countryside. Có nhiều khí thải nông nghiệp thành phố hơn nông thôn. Nowadays people spend _____more_______ money on education than in the past. Ngày nay mọi người dành nhiều tiền vào giáo dục hơn trong quá khứ. I hope this year we will harvest ____more________ rice than last year, so we won’t be worried about famine. Tôi hy vọng rằng năm nay chúng ta sẽ thu hoạch nhiều lúa gạo hơn năm ngoái, vậy chúng ta sẽ không lo về nạn đói Many people are moving to the city because there are __more____ job opportunities there than in the countryside. Nhiều người đang di chuyển về thành phố vì ở đó có nhiều cơ hội việc làm hơn ở nông thôn. The governments are trying to raise the living standards of people. I think that there will be _____fewer____ slum areas in the future. Chính phủ đang cố gắng nâng cao mức sống của mọi người. Tôi nghĩ rằng sẽ có ít khu ổ chuột hơn trong tương lai. Underdeveloped countries have to deal with ______more______ problems than developed countries. Những nước chưa phát triển phải đối mặt với nhiều vấn đề hơn các nước phát triển. Bài 3: Nối mệnh đề ở cột A với mệnh đề ở cột B sao cho hợp lý. A B This year, we grow more in the city than in the countryside. Fresh graduates often have less exciting experiences than his friends. There are fewer tree pets than anyone else in her class Jim has more working experience than other employees. Today Jane shows less flowers than we grew last year. My brother has to cope with more sheep in the farm now than before. Joana owns more problems than me. There are more confidence than she usually does. __a_____ 2- ____d___ 3- ____a___ 4-__b_____ 5- ___h____ 6-____g___ 7-___b____ 8- _______ Bài 4: Dựa vào câu cho trước, viết câu so sánh với “more/less/fewer”. Today I ate one slide of bread. Today I ate less bread than yesterday. My school has about two thousand students. Jane’s school has more than three thousand student. àMy school has fewer students than Jane’s school. Trường tôi có khoảng 2000 học sinh. Trường của Jane có hơn 3000 học sinh. Trường tôi có ít học sinh hơn trường Jane. I have only one science book but my brother has up to ten science books. à I have fewer science books than my brother. Tôi chỉ có một quyển sách khoa học nhưng anh tôi có hẳn 10 cuốn. àTôi có ít sách khoa học hơn anh tôi. There is only one library in her town but there are many libraries in my city. àThere are fewer libraries in her tow than in my city. àChỉ có một thư viện ở thị trấn của cô ấy nhưng có rất nhiều thư viện ở thành phố của tôi àCó ít thư viện ở thị trấn của cô ấy nhưng có rất nhiều thư viện ở thành phố của tôi. Yesterday I drank too much wine but Jane just drank a little. àYesterday I drank more wine than Jane. Hôm qua tôi uống quá nhiều rượu nhưng Jane chỉ uống có một chút. àHôm qua tôi uống nhiều rượu hơn Jane. We can find several skyscrapers in the city but we hardly find one in the rural area. àWe can find more skycrapers in the city than in the rural area. Chúng ta có thể tìm thấy rất nhiều tòa nhà chọc trời ở thành phố nhưng chúng ta hiêm khi nhìn thấy một cái ở vùng nông thôn. àChúng ta có thể tìm thấy rất nhiều tòa nhà chọc trời ở thành phố hơn ở nông thôn. I think you can finish two tasks and Jane can finish one task today. à I think you can finish more tasks than Jane today. Tôi nghi bạn có thể hoàn thành 2 nhiệm vụ và Jane có thể hoàn thành 1 nhiệm vụ hôm nay. àTôi nghĩ bạn có thể hoàn thành nhiệm vụ hơn Jane hôm nay. Maria has been to 4 countries in the world and I have been to 6 countries. àMaria has been to fewer foreign countries than I Maria đã từng đến 4 quốc gia và tôi đã tưng đến 6 quốc gia. àMaria đã từng đến ít quốc gia hơn tôi. This week my mother bought 3 littles of milk. Last week she bought 6 littles. à This week my mother bought less milk than last week. Tuần này mẹ tôi mua 3 lít sữa. Tuần trước mẹ tôi mua 6 lít. àTuần này mẹ tôi mua ít sữa hơn tuần trước. My watch cost a lot of money but her watch was even more expensive than mine. àMy watch cost less than her watch. Đồng hồ của tôi tốn rất nhiều tiền nhưng đồng hood của cô ấy còn đắt hơn của tôi. àĐồng hồ của tôi tốn ít tiền hơn đồng hồ của cô ấy This year they will plant two hundred trees along the streets. Last year they only planted one hundred trees. à This year they will plant more trees than last year. Năm nay họ sẽ trông 200 cây dọc những con đường. Năm ngoái họ chỉ trồng 100 cây. àNăm nay họ sẽ trồng nhiều cây hơn năm ngoái Bài 5: Gạch chân lỗi sai trong các câu sau đây và sửa lại cho đúng. Now there are more people in this village as in the past. Lỗi sai as à than Giải thích: Cấu trúc so sánh hơn “ .+more+ than+ ..” Jonh has more patient than I expected. Lỗi sai: patient à patience Giải thích: Cấu trúc so sánh .+ more + danh từ + than + .Patient là tính từ cần chuyển về danh từ là “ patience” My brother’s house has fewer modern equipments than mine. Lỗi sai: fewer modern equipmentsàless modern equipment Giải thích “ equipment” là danh từ không đếm được nên dùng less Today Kim showed fewer confidence than usual. feweràless Giải thích: confidence là danh từ không đếm được nên dùng “ less” There are fewer mouse in this house than there used to be. mouseàmice Giải thích: sau more là danh từ đếm được dạng số nhiều. There fishermen caught less fish yesterday than usual. lessàfewer Giải thích: fish là danh từ đếm được dạng số nhiều nên dùng “ more” You may have to face more problem than your colleague. problem àproblems sau more là danh từ đếm được ở dạng số nhiều. Jim has less time to complete his assignment than. than àbỏ than Giải thích: Trong câu này được lưu bởi một đối tượng so sánh nên than “ than” cũng cần được lược bỏ. CÂU HỎI ĐUÔI (TAG QUESTIONS) Định nghĩa và cách dùng Định nghĩa Câu hỏi đuôi là một câu hỏi ngắn, được thêm vào cuối câu trần thuật, đứng đằng sau dấu phẩy. Ví dụ: You like mushrooms, don’t you? (Bạn thích nấm phải không?) He isn’t a doctor, is he? (Anh ấy không phải là một bác sĩ phải không?) It’s a table, isn’t it? (Nó là một cái bàn phải không?) Cách dùng Trong văn nói, ý nghĩa của câu hỏi đuôi tùy thuộc vào cách diễn đạt. Nếu xuống giọng ở câu hỏi đuôi thì có nghĩa là không thật sự đặt câu hỏi, chỉ muốn người nghe đồng ý với mình. Nếu lên giọng ở câu hỏi đuôi, thì đó là câu hỏi thực sự. Cách thành lập câu hỏi đuôi tương ứng với các mệnh đề trần thuật Cấu trúc Auxiliary/ To be/ Modal verb (not) + Subject Trong đó Auxiliary(trợ động từ) như do/ dose/did, have/has Động từ tobe: am/ is/ are, was/were Modal verb (động từ khuyết thiếu) như can, could, must Subject (chủ ngữ) như he, she, it Trường hợp 1 Nếu câu trần thuật là câu khẳng định, câu hỏi đuôi phải ở thể phủ định. Hình thức phủ định thường được rút gọn (not = n’t) Ví dụ: She is reading book, isn’t she? (Cô ấy đang đọc sách, phải không?) Mr. Nam can speak English well, can’t he? (Ông Nam có thể nói tiếng Anh tốt, phải không?) They did the test yesterday, didn’t they? (Họ đã làm bài kiểm tra vào hôm qua phải không?) Your sister can swim, can’t she? (Chị gái của bạn biết bơi, phải không?) Trường hợp 2 Nếu câu trần thuật là câu phủ định, câu hỏi đuôi phải ở thể khẳng định. Ví dụ: Nga isn’t a student, is she? (Nga không phải là học sinh, phải không?) I shouldn’t smoke here, should I? (Tôi không nên hút thuốc ở đây, phải không?) Her parents don’t work in this company, do they? (Bố mẹ cô ấy không làm việc ở công ty này, phải không?) They don’t have to go to school, do they? (Họ không phải đi tới trường phải không?) Chú ý Nếu trong câu trần thuật có trợ động từ hoặc động từ to be thì trợ động từ này được lặp lại trong câu hỏi đuôi. Ví dụ: She was a writer,wasn’t she? Miss Lan will go to Ho Chi Minh next month, won’t she? They didn’t meet him last night, did they? Nếu câu trần thuật không có trợ động từ, dùng trợ động từ tương ứng với thì của câu trần thuật như do/ dose/did, have/has He lives in Hanoi city, doesn’t he? You came here, didn’t you? They watch TV every evening, don’t they? Trường hợp đặc biệt Câu hỏi đuôi của I am là aren’t I- nhưng nếu là I am nôt thì vẫn dùng am I? Ví dụ: I am wrong, aren’t I? (Tôi sai, phải không?) I’m not wrong, am I? (Tôi không sai, phải không) Câu trả lời đối với dạng câu hỏi đuôi Yes nếu đồng ý với câu trần thuật ở trên. No nếu không đồng ý với ý kiến ở câu trần thuật. Ví dụ: Your sister is married, isn’t she? Yes, she has just married./ No, of couse she isn’t. Tuy nhiên, cần chú ý câu trả lời Yes/No trong câu trả lời đối với câu hỏi phủ định. Ví dụ: You’re not going out today, are you? (Hôm nay bạn không đi chơi phải không?) Yes. (=Yes, I am going out) Có. (Có, tôi có đi chơi) No. (No, I am not going out) Không. (= Không, tôi không đi chơi) Các bước lần lượt thành lập câu hỏi đuôi Bước 1: Xác định thì của mệnh đề chính. Bước 2: Xác định loại động từ có trong câu: động từ thường, động từ khuyết thiếu hay động từ to be. Bước 3: Xác định mệnh đề chính là câu khẳng định hay phủ định. Nếu mệnh đề chính là câu khẳng định câu hỏi đuôi là câu phủ định. Nếu mệnh đề chính là câu phủ định câu hỏi đuôi là câu khẳng định. Bước 4: Thay đổi đại từ trong câu hỏi đuôi nếu cần. Dưới đây là một vài ví dụ: Câu trần thuật phủ định, câu hỏi đuôi khẳng định. Câu trần thuật khẳng định, câu hỏi đuôi phủ định. You aren’t a teacher, are you? You are a student, aren’t you? He isn’t crazy, is he? He is very busy, isn’t he? They weren’t late, were they? They were surprised, weren’t they? You don’t speak French, do you? You speak English, don’t you? You haven’t been here all week, have you? You have studied all week, haven’t you? You won’t fail the exam, will you? You will pass the exam, won’t you? She can’t drive a car, can she? She can speak two languages can’t she? We mustn’t say anything, must we? We must be patient, mustn’t we? BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN Bài 6: Điền một chủ ngữ thích hợp vào chỗ trống để hoàn thành các câu hỏi đuôi sau. They are going home from school, aren’t they_? John didn’t do the washing yesterday, did __he__? We couldn’t buy a new car, could ___we____? Kevin will arrive here before 4 o’clock, won’t ___he___? I am not good- looking, am ____I ____? James is from England, isn’t ___he___? The car isn’t in the garage, is __it__? You are Ann, aren’t __ you ___? His father took him to the zoo yesterday, didn’t ___he____? Our neighbors have moved here, haven’t ___they ____? Giải thích: Nếu chủ ngữ ở câu trần thuật là I, you, we, he,she , it thì trong phần câu hỏi đuôi lặp lại những chủ ngữ đó. Nếu chủ ngữ là người ở ngôi thứ 3 số ít thì trong phần câu hỏi đuôi sử dụng đại từ nhân xưng t” he” “ she” làm chủ ngữ, nếu là vật thì dùng “ it” Trong trường hợp chủ ngữ là danh từ không đếm được thì dùng” it “ Nếu chủ ngữ là ngôi thứ 3 số nhiều thì trong phần câu hỏi đuôi sử dụng đại từ nhân xưng dùng” they” làm chủ ngữ. Bài 7: Khoanh tròn vào đáp án đúng. She is collecting seashells, (is/isn’t) she? Giải thích: Mệnh đề trần thuật có động từ” to be” is ở thể khẳng định nên trong câu hỏi đuôi phải dùng thể phủ định là “ isn’t” We often play soccer in the afternoon, (do/don’t) we? Mệnh đề trần thuật có động từ thể khẳng định nên trong câu hỏi đuôi phải dùng thể phủ định. You weren’t recognized, (were/ weren’t) you? Mệnh đề trần thuật có động từ to be “weren’t” ở thể phủ định nên trong câu hỏi đuôi phải dùng thể khẳng định là were Your father (has/hasn’t) cleaned your bike, hasn’t he? Câu hỏi đuôi co động từ thể phủ định nên trong mệnh đề trần thuật phải dùng thể khẳng định John and Jim (like/don’t like) scary movies, don’t they? Câu hỏi đuôi co động từ thể phủ định nên trong mệnh đề trần thuật phải dùng thể khẳng định You (can/can’t) win this competition, can you? Câu hỏi đuôi có động từ thể khẳng định nên trong mệnh đề trần thuật phải dùng thể phủ định. She is watching TV downstairs, (isn’t/doesn’t) she? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ “ to be” is thì lặp lại “is” trong câu hỏi đuôi. The journey to the South cost a lot of money, (doesn’t/ didn’t) it? Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng địn thì quá khứ đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ phủ định “ didn’t” You won’t lie to me, (will/do) you? Câu trần thuật ở thể phủ định thì tương lai nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ to be ở thể khẳng định “will” Josh and John have met each other, (haven’t/don’t) they? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ “ have” ở thể khẳng định thì hiện tại hoàn thành nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ haven’t” She’s from a small town in Thailand, (doesn’t/isn’t)she? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ “ to be “ is” thì nên lặp lại “ is” trong câu hỏi đuôi. I am intelltgent, (amn’t / aren’t) I? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ “to be” are thì nên lặp lại “are” trong câu hỏi đuôi. We’re late again, (/ aren’t) we? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ” to be” are” thì nên lặp lại “are” trong câu hỏi đuôi. They are going to France this summer, (aren’t/ don’t) they? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ to be “ are” thì nên lặp lại are trong câu hỏi đuôi. She didn’t use to work in a hotel, (did/does) she? Trong câu trần thuật ở thể phủ định thì quá khứ đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể khẳng định “ did” You must obey the rule, (don’t/mustn’t) you? Trong câu trần thuật dùng động từ khuyết thuyết ở thể khẳng định “ must” nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng động từ khuyết thuyết ở thể phủ định “ musn’t” . They need some new clothes, (needn’t/ don’t) they? Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định thì hiện tại đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ don’t” Jim and his wife live in a tiny flat, (doesn’t/ don’t) they? Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định thì hiện tại đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ don’t” Mary studies very hard every night, (doesn’t/ did) she? Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định thì hiện tại đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ doesn’t” This table is made wood, (isn’t/ doesn’t) it? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ to be “ is” thì nên lặp lại “ is” trong câu hỏi đuôi. There are 30 students in your class, (aren’t/ don’t) there? Trong câu trần thuật có động từ to be “ are” thì nên lặp lại “ are” trong câu hỏi đuôi You shouldn’t take in too much sugar, (do/ should) you? Trong câu trân thuật dùng động từ khuyết ở thể phủ định “ shouldn’t” nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng động từ khuyết thiếu ở thể khẳng định “ should” David and James will be learning Japanese at this time next week, (aren’t/ won’t) they? Trong trần thuật ở thể khẳng định thì tương lai đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ won’t” She doesn’t cook very often, (do/does) she? Câu trần thuật ở thể phủ định thì hiện tại đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể khẳng định” does” Jim hurt this leg yesterday, (doesn’t/ didn’t) he? Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định thì quá khứ đơn nên trong câu hỏi đuôi dùng trợ động từ ở thể phủ định “ didn’t” Bài 8: Điền các câu hỏi đuôi cho sẵn vào chỗ trống sao cho hợp lý. aren’t don’t we is she does he will they is she did it won’t they wasn’t he isn’t she Your parents will pick you up today, ___ won’t they _________? Chủ ngữ “ your parents” trong câu trần thuật chuyển về chủ ngữ “ they” trong câu hỏi đuôi. Câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định câu hỏi đuôi ở thể phủ định. Câu ở thì tương lai đơn nên dùng trợ động từ “ won’t” ở câu hỏi đuôi. Mary isn’t sleeping now, ___ is she _________? Chủ ngữ “Mary” trong câu trần thuật chuyển về chủ ngữ “ she” trong câu hỏi đuôi. .Câu trần thuật ở thể phủ định nên câu hỏi đuôi ở thể phủ định. Câu trần thuật có động từ to be “ is” nên dùng “ isn’t” ở câu hỏi đuôi. My cat didn’t come home yesterday, ___ did it _________? Chủ ngữ “my cat” trong câu trần thuật chuyển về chủ ngữ “it” trong câu hỏi đuôi My brother was ill yesterday, ____ wasn’t he ________? I am right, _____ aren’t I ____? We often go fishing in the weekend, ____ don’t we ________? They won’t destroy this building, ____ will they ________? Jim doesn’t like collecting stamps, ____ does he ________? Your grandmother is watering flowers, ____ isn’t she ________? She isn’t your sister, ____ is she ________? Bài 9: Hoàn thành các câu hỏi đuôi sau đây. It is your cat, ____isn’t it________? This umbrella is yours, _____isn’t it _______? You won’t leave the party early, ____will you ________? We went to a Japanese restaurant yesterday, _____didn’t we_______? You mustn’t press this button, ___must you_________? They haven’t found their keys, ____have they ________? Anne and Tom often play badminton with each other, _____don’t we___? Peter is listening to music upstairs, ____isn’t he ________? The students must finish their homework, __must he__________? It will be snowing at this time next week, ____won’t it ________? I can leave now, _____can’t I _______? My classmates and I will be learning English at 8 a.m, tomorrow, ___won’t we__? You didn’t attend the meeting, ___did you_________? The sheep are grazing in the fields, ____aren’t they ________? Josh should pay attention to his health condition, ____shouldn’t he_______? His father was an employee of this company ten years ago, __wasn’t he_____? My mother doesn’t like my untidiness, ___does she_________? James will go camping with us tomorrow, ____won’t he________? Your bike is broken, ______isn’t it ______? You were terrified by the thunder, _____weren’t you_______? They didn’t expect me to appear at the meeting, __did they____? It is important to be on time, ___isn’t it_________? This doctor hasn’t worked in the local hospital for 2 months, ____has he______? We have been to New York, ____haven’t we________? James could win the match yesterday, ____couldn’t he________? Bài 10: Đánh dấu [√] trước câu đúng. Đánh dấu [X] trước câu sai và sửa lại cho đúng. ____ X _____ 1. You can afford time to come to our party, can you? Can you à can’t you: câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định nên câu hỏi đuôi ở thể phủ định ____ X _____ 2. He put sugar on my coffee, doesn’t he? Doesn’t he à didn’t he. Câu ở thì quá khứ đơn nên dùng trợ động từ “didn’t” ____ X _____ 3. They won’t let me take photos here, will I ? I à they chủ ngữ they trong câu trần thuật được láy lại trong câu hỏi đuôi. _____ X ____ 4. This song is catchy, isn’t this? Isn’t this àisn’t it : chủ ngữ this song trong câu trần thuật chuyển về chủ ngữ it trong câu hỏi đuôi. ____ X _____ 5. Your mother’s bought you a new dress, isn’t she? Isn’t à hasn’t: câu ở thì hiện tại hoàn thành nên dùng trợ động từ “ hasn’t” ______√___ 6. Someone mistook you for a famous singer, didn’t they? ____ X _____ 7. Josh practices singing every day, does he? Doesà doesn’t : câu trần thuật ở thể khẳng định nên câu hỏi đuôi ở thể phủ định. ____√_____ 8. There isn’t any parks near here, is there? BÀI TẬP TỔNG HỢP NÂNG CAO Bài 11: Dựa vào những thông tin có trong bảng cho sẵn, sử dụng “more/less/fewer” để so sánh trường học của Jane và Peter. Number of Jane’s school Peter’s school Student 2 thousand 1.5 thousand Building 5 4 Classroom 280 190 Classroom equipment Computer, projector, ceiling fans Computer, projector, loudspeakers, air- con, fans Student club 6 9 Time for self- studying 10 hours a week 8 hours a week Jane’s school has fewer students than Peter’s school. Jane’s shool has more buildings than Peter’s school. Jane’s shool has more classrooms than Peter’s school. Jane’s shool has less classroom equipment than Peter’s school. Jane’s shool has fewer student clubs than Peter’s school. Jane’s shool has more time for self-studying than Peter’s school. Dựa vào thông tin trong bảng thông tin và số lượng trong bảng thống kế để xác định dùng “ more” ( so sánh hơn) hay les/fewer ( so sánh kém) , “less” dùng trong những danh từ không đếm được, fewer dùng với danh từ đếm được ở dạng số nhiều Bài 12: Hoàn thành câu thứ hai sao cho nghĩa không đổi so với câu thứ nhất, sử dụng “more/less/fewer”. There are more street lights on this road than that road. There are fewer street lights on that road than this road. There were fewer criminal cases in my country 3 years ago than now. à There are more criminal cases in my country now than 3 years ago. There are more wealthy people in big cities than in the countryside. àThere are fewer wealthy people I the countryside than in big city. My city has fewer slums than yours. à Your city has more slums than mine The standards of living in the cities shows more improvement than in the rural areas. à The standards of living in rural areas shows less improvement than in the cites. Old factories produce more carbon dioxide emissions than modern factories. àModern factories produce fewer carbon dioxide emissions than old factories. There are less arable land in the city than in the countryside. à There are more arable land in the countryside than in the city. Are there more health centres in my city now than ten years ago? àWere there fewer healthy centres in my city ten years ago than now? People in developed countries spend more money on health care and education than in the underdeveloped countries. àPeople in the undevelop countries spend less money on health care and education than in develop country. Bài 13: Hoàn thành các câu hỏi đuôi sau: No one will reveal my secrets, ___will they ____? Everyone in the room is staring at me, ___aren’t they _________? A bridge will be built here next year, ____won’t it________? There aren’t any slums in your city, ____are there________? Someone has eaten my cake, ______haven’t they ______? The Smiths will travel back to their hometown next summer, ____won’t they _______? There will be more skyscrapers in our city, ___won’t there _________? You have been to Paris, ___have you _______? Jim should do more research on this topic, ___shouldn’t he _______? In the past, rabies was an incurable disease, ____wasn’t it _____? A conference on population explosion will be held tomorrow, ___won’t it ___? You didn’t use to walk to school, ____did you____? Your pets are fed by your mom everyday, ____aren’t they _____? Air pollution is caused by carbon dioxide emissions from factories and vehicles,__isn’t it_? You used to be a teacher, ____didn’t you________? Bài 14. Dựa vào những từ cho sẵn, viết mệnh đề trần thuật và câu hỏi đuôi của nó. You/ go shopping/ with your mother tomorrow. You will go shopping with your mother tomorrow, won’t you? Mr. Smith/ not come/ home/ yesterday. Mr.Smith didn’t home yesterday, did he? Your parents/ be/ at home/ now. à Your parents are at home now, aren’t there? It/ not rain/ tomorrow. It won’t rain tomorrow, will it? Jim/ not do/ his homework/yet. Jim hasn’t done his homework yet, has he? Jane’s cat/ sleep/ now. Jane’s cat is sleeping now, isn’t it? Mary and Jim/ can/ speak/ both English and French. àMary and Jim can speak both English and French, can’t they? Peter/ live/ here/ for 5 years. Peter has live here for 5 years, hasn’t he? These shoes/ cost/ a lot of money. àThese shoes cost a lot of money, don’t they? You sisters/ look after/ your grandparents/ now. Your sisters are looking after your grandparents now, aren’t they? I/ must/ go home/ now. I must go home now, mustn’t I? Bài 15: Khoanh tròn đáp án đúng. Favela “Favela” is the Portuguese word for “slum” in Brazil in one of the (1)__________ economically unequal countries in the world. Favelas(2) __________ associated with extreme poverty. They earn much(3) __________ money than other people. Residents of favelas are often discriminated (4) __________ they live in these communities. They have (5) __________ chance of experiencing inequality and exploitation than the upper classes. Moreover, the cocaine trade has affected Bazil and (6)v favelas. A favela can (7) __________ ruled by a drug lord. The Brazil government has made attempt to improve the living (8) __________ of slums’ redidents in 20th century. A. most B. more C. fewer D. less A. is B. are C. do D. did A. most B. more C. fewer D. less A. Despite B. Although C. Because D. However A. most B. more C. fewer D. less A. its B. it C. theirs D. their A. is B. was C. been D. be A. levels B. classes C. standards D. grades Bài 16: Đọc đoạn văn sau và trả lời các câu hỏi dưới đây. Over the years, overpopulation has posed major threat to our fragile environment. Its effects are quite severe. One of the most obvious consequences is that natural resources will soon be used up. As the human population continues to explode, fininnte natural resources, such as fossil fuels, fresh and frontier forests continue to plummer. If the number of people continues to rise uncontrollably, the available resources won’t not meet the demand of people. Moreover, because of the overuse of coal, oil and natural gas, human has caused some serious pollution. The huge numbers of vehicles and factories have polluted the air, land and even water. Rise in
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 giao_an_tieng_anh_khoi_7_bai_12_an_overcrowded_world_mot_the.docx
giao_an_tieng_anh_khoi_7_bai_12_an_overcrowded_world_mot_the.docx



